Bacterial Profile and Their Antimicrobial Susceptibility Pattern of Isolates Recovered from Intensive Care Units of Libyan Hospitals.
- Authors
-
-
Ahmed Alsharksi
Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Medicine, Misurata University, LibyaAuthor -
Abdalla Ali
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Education, Misurata University, LibyaAuthor -
Adam Mustapha
Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Life Sciences, University of Maiduguri, NigeriaAuthor -
Muna Alshagmani
Department of Medical Laboratory, Alyaqen Medical Science College, Misurata, LibyaAuthor
-
- Keywords:
- Hospital-Associated Infection, Antibiotic Resistance, ICU, Public Health, Misurata, Libya.
- Abstract
-
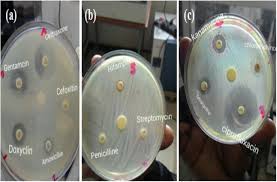
Presence of Bacterial contamination in hospital environments, particularly intensive care units, poses a serious threat to global public health in the world with high morbidity and mortality rates. Of more concern is the emergence of multidrug-resistant bacteria on medical devices, inanimate surfaces, health care providers, and patients in the intensive care unit, which could lead to further cross-contamination and infection. This study aimed to assess the bacterial profile and their antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of bacterial isolates from the intensive care unit of the Emergency unit, internal medicine, and coronary unit of Misurata Central Unit of Misurata, Libya. A unit-based cross-sectional study was conducted on three Intensive Care units from 1st December 2024 to 27th December 2024. In this project, a total of 102 swab samples from the intensive care unit environment were collected using cotton swabs. Standard Microbiological techniques to include culture method and Gram stain, were employed for the identification of the isolates. Antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacterial isolates were performed by using the Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion method. In the total of 102 swab samples, bacterial growth was observed in 19.6% (20/102) of the total samples. Out of the total bacterial growth recovered, the Coronary care unit had the highest, 50% (10/20), followed by the Emergency unit 35% (7/20), and the Internal medicine unit had 15% (3/20). The most frequently found isolate was Staphylococcus aureus 75% (15/20), followed by Streptococcus pyogenes 15% (3/20), Pseudomonas aeruginosa 5% (1/20), and E coli 5% (1/20). Results of the antibiotic susceptibility pattern revealed that most of the isolates are multidrug-resistant. Results from this study showed bacterial contamination of the ICU environments and their resistance patterns, which suggest that patients are prone to hospital-associated infection. It is recommended that strict sterilization of intensive care units be standardized and the hygiene of hospital workers be enforced to prevent transmission of infection in hospital environments.
- References
- Cover Image
-
- Downloads
- Published
- 2025-08-02
- Issue
- Volume 1, Issue 3, 2025
- Section
- Articles
How to Cite
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- Ahmed Alsharksi, Abdalla Ali, Adam Mustapha, Clostridium difficile A-B Toxins as a Cause of Diarrheal Disease: Data from a University Hospital in Northern Cyprus , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 4, 2025
Similar Articles
- Wadiaa Benamer, Tamader Elghnimi, Mustafa Targhi, Loujain Husnein, Ussra Ben Enbaya, Women's Awareness of Contraceptives in Tripoli City: A Field Study , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 3, 2025
- Najwa Belhamad, Boshra Fathalla, Marfoua Ali, Prevalence and Risk Factors of Urinary Tract Infection among Pregnant Women Attending Antenatal Clinics at Some Private Sectors in El Jabal Al Akhdar, Al-Byda, Libya , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 2, Issue 1, 2026
- Mufeedah Mansour, Khoulah Alaribi, Prevalence and Outcomes of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci in Newborns Admitted to the NICU in a Tertiary Hospital in Libya , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 2, 2025
- Mariam Alqasser, Stroke Incidence and Risk Profile in Misrata City: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Hospital-Based Study from Emergency Medical Records (2019–2020) , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 4, 2025
- Khiloud Amin, Enas Ramih, Rodaba Bitrou, Najat Alrumayh, Mohamed Emhemed, Abdallah Juwid, Abdsalam Rabie, Monsef Algouti, Mussa Alragig, Mohamed Elfagieh, Eramah Ermiah, Prognostic Value of KRAS Mutation Status in Libyan Patients with Colorectal Cancer , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 2, Issue 1, 2026
- Dania ELhassan , Mohanned Alwashaish , Salma Lajhar, Aya Aldiab , Khadija Safar, Prevalence, Biofilm Formation, and Antimicrobial Resistance of Uropathogens Isolated from Patients with Urinary Tract Infections in Misurata, Libya , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 4, 2025
- Faiza Nouh, Salima Elfagi, Mohamed Buzqeia, Ahlam Adel, Mawadda salah, Enas Hassan, Safa Edress, Determinants of Food Choices in University Cafeterias: A Cross-Sectional Study Among Public Health Students in Libya , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 4, 2025
- Omar Alhaddad, Tasneem Shneshah, Safa Alzuwawi, Sarah Alkuawylidi, Lamis Mafa, Assessment of Hand hygiene knowledge Among Undergraduate Medical Students and Intern Doctors in Misurata University, Libya: A Cross-Sectional Study , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 3, 2025
- Wesam Elsaghayer, Wafaa Babh, Ali Shagan, Misbah Elfagih, Esraa Obida, Ebrahim Elmahjoubi, Mohamed Bashagha, Mohamed Elfagieh, Sentinel Lymph Node Metastasis in Breast Cancer: The First Libyan Report with Hormonal Profiling and International Comparison , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 3, 2025
- Marfoua Ali, Faraj Sulayman, Elham keeshar, General Health Parameters in Children Aged 6–10 Years in El‑Beyda, Libya , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 2, Issue 1, 2026
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.








