Identification and Evaluation of Drug-Related Problems in Patients with Reduced Kidney Function: A Retrospective Study
- Authors
-
-
Nadia Alrawaiq
General Department, Faculty of Pharmacy, Sebha University, Sebha, LibyaAuthor -
Fatima Younis
General Department, Faculty of Pharmacy, Sebha University, Sebha, LibyaAuthor -
Mabrouka Ismail
General Department, Faculty of Pharmacy, Sebha University, Sebha, LibyaAuthor
-
- Keywords:
- Chronic Kidney Disease, Comorbidities, Drug‑Related Problems, Polypharmacy.
- Abstract
-
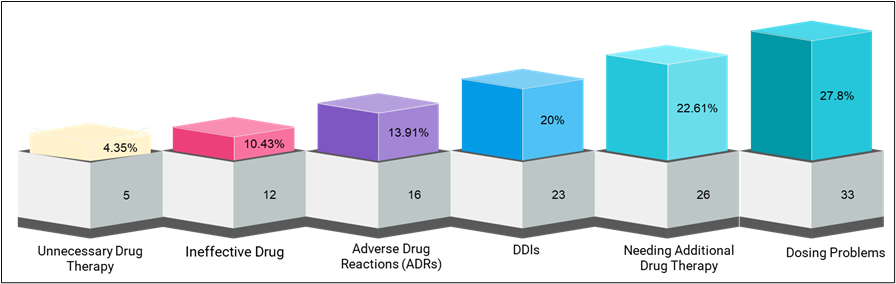
Patients with reduced kidney function are at an increased risk for complex drug-related problems due to altered drug pharmacokinetics and the presence of multiple comorbidities. This study aimed to identify and evaluate drug-related problems (DRPs) in this vulnerable patient population to enhance pharmacotherapy management. A retrospective analysis was performed on a cohort of 60 patients with reduced kidney function. Demographic and clinical data, including age, gender, and the number of comorbidities, were collected. Medication-related issues were categorized and quantified, focusing on unnecessary drug therapy, dosage concerns, the need for additional therapy, ineffective drugs, adverse drug reactions (ADRs), and drug-drug interactions (DDIs). In this study, a total of 60 patients with low kidney function were evaluated, whose average age was 63 ± 2.39 years. The most frequently represented age groups were 60–69 and 70–79 years (each 13 patients), followed by the 80–89-year-old group (10 patients). The study consisted of 23 males (38.3%) and 37 females (61.7%), with an average of 3.4 Comorbidities per patient. A detailed analysis of the drug-related issues was conducted, in which several notable conclusions were detected. First, unnecessary drug therapy was identified in five cases (4.35%). Secondly, dosage-related issues were important, with 23 examples where the dose was too high (20%) and 10 examples where the dosage was very low (8.70%). Third, an additional drug therapy requirement was noted in 26 cases (22.61%). Finally, ineffective drugs were identified in 12 cases (10.43%). 16 examples (13.91%) reported adverse drug reactions (ADRs), while drug-drug interactions (DDIs) were seen in 23 examples, accounting for 20% of the total incidents. The study emphasizes considerable proliferation of drug complications among patients with low renal function, mainly due to dosage-related issues and the need for additional medications. Conclusions emphasize the importance of individual and careful drug management in this demographic, which aims to reduce deformed results and to improve medical efficacy.
- References
- Cover Image
-
- Downloads
- Published
- 2025-09-01
- Issue
- Volume 1, Issue 3, 2025
- Section
- Articles
How to Cite
Similar Articles
- Mohanad Al-Ghanimi, Manaf Yaseen, Wassan Nori, Unexpected Vascular Anomaly; Right Subclavian-Pulmonary Artery Connection Unraveled during Routine PDA Closer; Case Report , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 3, 2025
- Adell Abubakeer, Nabel Mansour, The Association Between ABO and Rhesus Blood Groups and Diabetes Mellitus in Libya: A Systematic Review of National Evidence , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 3, 2025
- Raja Moman, Nouralhuda Altair, Abdulkarem Tamer, Amnnah Ghalbun, Nagat EL-Magrahi, Antibiosis of Antibiotics, Honey and Probiotics Related Bacteria to Diabetic Foot Infections , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 1, 2025
- Omar Alhaddad, Tasneem Shneshah, Safa Alzuwawi, Sarah Alkuawylidi, Lamis Mafa, Assessment of Hand hygiene knowledge Among Undergraduate Medical Students and Intern Doctors in Misurata University, Libya: A Cross-Sectional Study , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 3, 2025
- Safaa Shehab, Hiba Awad, Shahrazad Khalaf, Zahraa Dawood, Sabaa Kareem, Fatima Salman, Blood-borne Viral Infections in Hemodialysis Units in Iraq: A Narrative Review of Prevalence and Contributing Factors , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 3, 2025
- Hosam Elarabi, Salem Salem, Rajaa Fadel, Wafa Abozaid, Abdullah Ahmad, Ahmed Shtawa, Moftah Ali, Assessment of Fluoride Concentration in Drinking Water and Its Correlation with Dental Caries in Primary School Children in Gharyan, Libya , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 2, 2025
- Zinab Elfituri, Huria Dardar, Yasmein Alshibani, Aml Koubas, Entisar Aboukanda, Abdalhalim Suaiee, The Impact of Lifestyle Factors on Arterial Blood Pressure and Its Control in Hypertensive Patients , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 2, 2025
- Shahrazad Ahmed, Neyaf Alageedi, Eman Muhsin, Doaa Abdulwahab, The Role of Immune Response in Bacterial Urinary Tract Infections in Iraq: A Review , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 2, 2025
- Hawa Abduljalil, Tarik Enaairi, Striae Gravidarum and Its Effect on the Quality of Life Index in Libyan Pregnant Women , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 1, 2025
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.








