The Importance of Probiotics in Human and Animal Life: A Review
- Authors
-
-
Alaa ALMoula
Department of Chemistry, College of Education for Pure Sciences, University of Kirkuk, IraqAuthor -
Lana Mansor
Department of Chemistry, College of Education for Pure Sciences, University of Kirkuk, IraqAuthor -
Sarmad Almaula
Department of Animal Production, College of Agriculture and Forestry, University of Mosul, IraqAuthor
-
- Keywords:
- Probiotics, Lactobacillus, Bifidobacteria, Saccharomyces, Good Bacteria
- Abstract
-
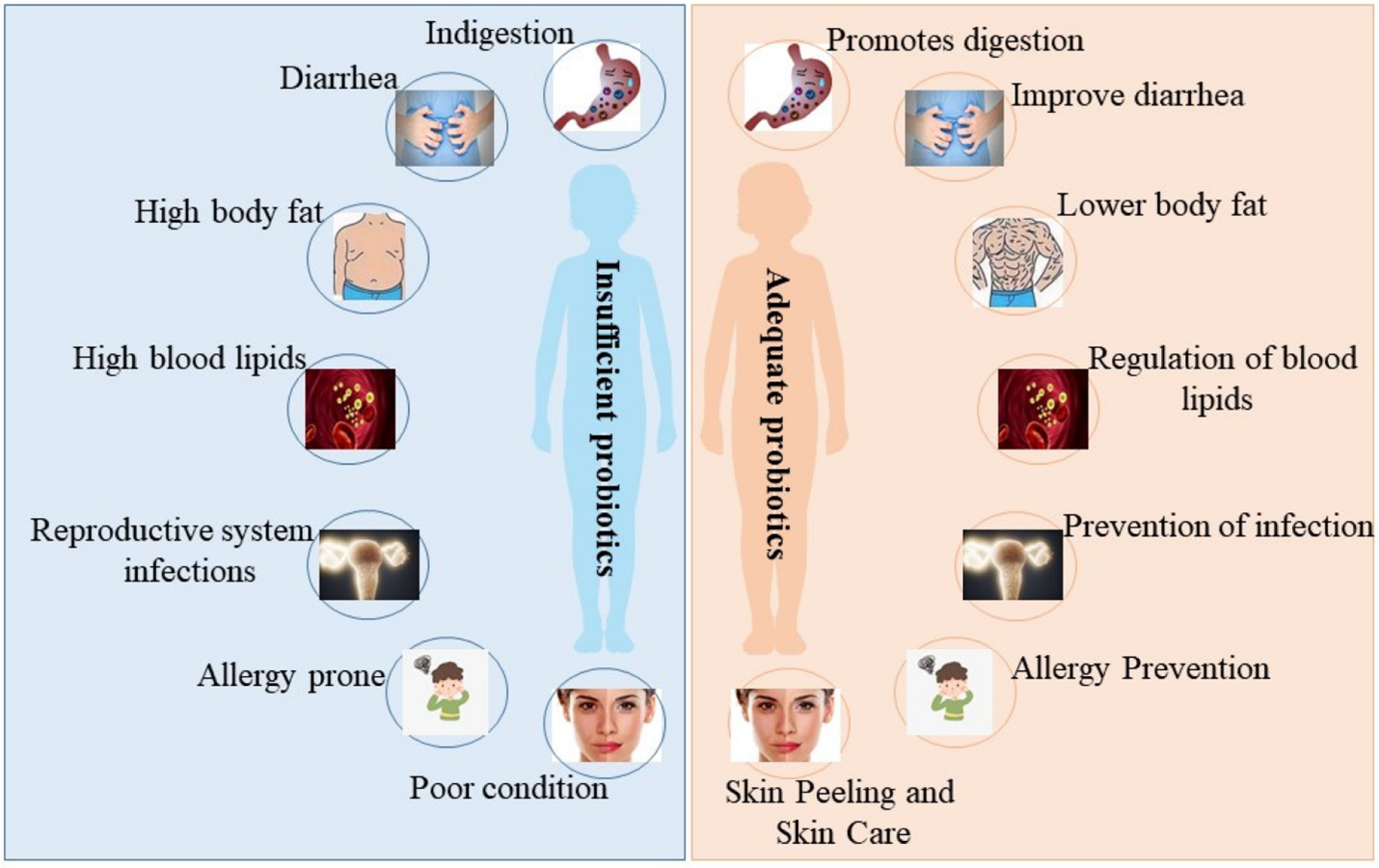
Probiotics are live bacteria that, when given in sufficient quantities, help the host's health. They have attracted much interest lately. These good bacteria, which typically include Lactobacillus, Bifidobacteria, and Saccharomyces, improve the health of both animals and humans. Antibiotics alter the body's natural microbiota and result in vitamin deficiencies because they cannot distinguish between healthy and bad bacteria. They also significantly reduce the host's defenses by killing beneficial bacteria in the vaginal and intestinal tracts. Because of their positive impacts on human health, including metabolism and immune function, probiotics—a colony of bacteria that reside in our intestines—are thought of as a metabolic "organ." In therapeutic contexts, they treat and prevent diseases like autism, migraine, Helicobacter pylori infection, colon cancer, hypertension, diabetes, acute pancreatitis, diarrhea, and ventilator-associated pneumonia. By enhancing gut barrier function, modifying microbial habitat in the intestine, boosting innate and adaptive immune responses, promoting competitive adhesion to the mucosa and epithelium, and generating antimicrobial chemicals, probiotics may change immunological activity. The purpose of this study is to list the important role that probiotics play in the prevention and therapeutic use of many diseases for which there may or may not be treatment options. A thorough search was conducted using keywords like probiotics, microbiota, prophylactics, and therapeutic uses in research databases like PubMed, PubMed Central (PMC), Scopus, Web of Science, Research Gate, Google Scholar, and the Cochrane Library. The main points of this succinct narrative review essay were the selection, history, mechanism/mode of action, most recent developments in therapeutic and preventative uses, and prospective avenues for probiotic use in medicinal and preventative purposes.
- References
- Cover Image
-
- Downloads
- Published
- 2025-11-29
- Issue
- Volume 1, Issue 4, 2025
- Section
- Articles
How to Cite
Similar Articles
- Raja Moman, Nouralhuda Altair, Abdulkarem Tamer, Amnnah Ghalbun, Nagat EL-Magrahi, Antibiosis of Antibiotics, Honey and Probiotics Related Bacteria to Diabetic Foot Infections , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 1, 2025
- Mohamed Zeglam, Mohamed Altier, Hala Alhawij, Mohamed Abuagila, A Cross-Sectional Assessment of Bacterial Contamination in Fixed Prosthodontic Impressions Transferred from Clinics to Dental Laboratories: A Study in Tripoli, Libya , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 3, 2025
- Dania ELhassan , Mohanned Alwashaish , Salma Lajhar, Aya Aldiab , Khadija Safar, Prevalence, Biofilm Formation, and Antimicrobial Resistance of Uropathogens Isolated from Patients with Urinary Tract Infections in Misurata, Libya , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 4, 2025
- Sara Fathi, Heba Hassan, Laila Alfageih, Prevalence of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae Isolated from Clinical Samples in Medical Tobruk Center , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 3, 2025
- Shahrazad Ahmed, Neyaf Alageedi, Eman Muhsin, Doaa Abdulwahab, The Role of Immune Response in Bacterial Urinary Tract Infections in Iraq: A Review , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 2, 2025
- Basheer Alhadheeri, Comorbidities and Treatment Outcomes of Acute Appendicitis at a Tertiary Center in Libya , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 3, 2025
- Nawfal Hussein, Liwar Ahmed, Halder Abozait, Antimicrobial Resistance in Iraq: A Public Health Emergency in the Shadow of Conflict , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 3, 2025
- Shahad Alwan, Molecular detection of the MexA efflux pump gene in Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from Diyala Province , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 3, 2025
- Ahmed Alsharksi, Abdalla Ali, Adam Mustapha, Muna Alshagmani, Bacterial Profile and Their Antimicrobial Susceptibility Pattern of Isolates Recovered from Intensive Care Units of Libyan Hospitals. , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 3, 2025
- Nowar Bhari, Hamed Bogdadi, Shamsi Saad, Fagonia glutinosa from Libya as a Potential Source of Lead Compounds: GC-MS Characterization of Metabolites with Antimicrobial and Anticancer Activities , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 3, 2025
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.








