Understanding the Hidden Immune Evasion Mechanisms by Cancer Cells and Therapeutic Approaches
- Authors
-
-
Marwah Rasah
Department of Zoology, Faculty of Arts and Sciences, Gharyan University, LibyaAuthor -
J. M. Jbireal
Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, Sabratha University, Libya. Knowledge Center for Scientific Consultation, Academic Services, and Research, Sabratha, LibyaAuthor
-
- Keywords:
- Cancer Immunotherapy, Immune Escape, Tumor Microenvironment, Cancer Vaccines, Adoptive T-cell Therapy
- Abstract
-
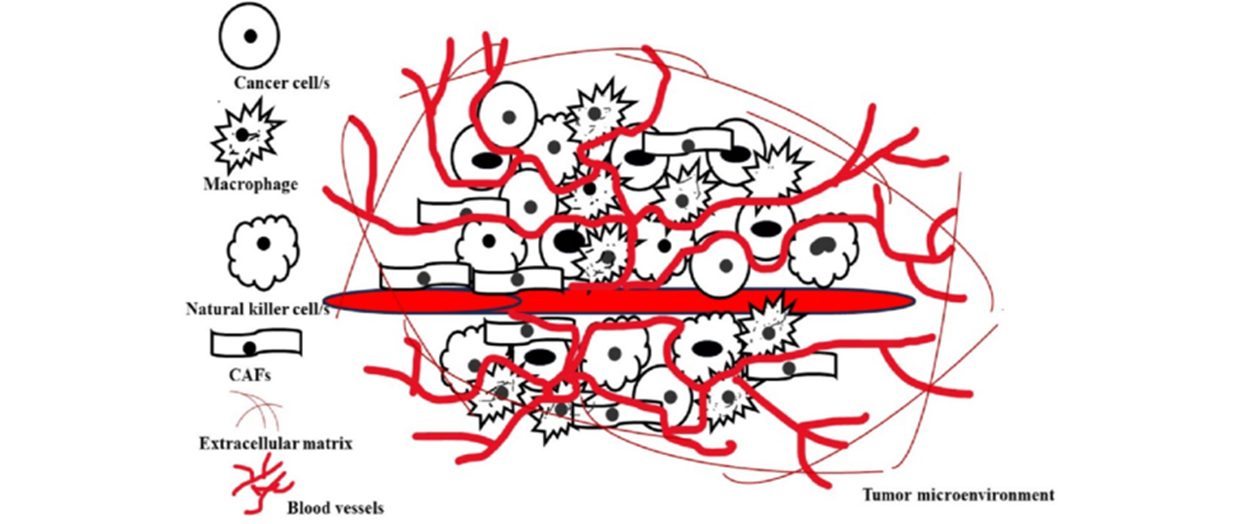
The immune system plays a fundamental role in recognizing and eliminating malignant cells to maintain cellular homeostasis. However, the tumor microenvironment (TME), composed of tumor and stromal cells, extracellular matrix, vascular components, and soluble mediators, promotes cancer progression by enabling immune escape mechanisms. Advances in cancer immunology have led to the development of various immunotherapeutic strategies designed to restore antitumor immune responses. These include monoclonal antibodies that selectively target tumor-associated antigens, therapeutic cancer vaccines that stimulate durable immune protection, and adoptive cell therapies that enhance tumor-specific T-cell activity. Although these approaches have shown significant clinical benefits, immune suppression within the TME continues to limit treatment efficacy. A deeper understanding of immune checkpoint pathways and tumor-induced immune dysfunction is therefore essential to improve current therapies and guide future innovations in cancer management.
- References
- Cover Image
-
- Downloads
- Published
- 2025-12-15
- Issue
- Volume 1, Issue 4, 2025
- Section
- Articles
How to Cite
Similar Articles
- Malak Eljafari, Ebtihal Franda, Analgesic Effect of Ethanolic Buthus occitanus Tail Extract in Albino Mice , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 2, Issue 1, 2026
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.








