Evaluation of Uterine Fibroids Among Women in Tripoli
- Authors
-
-
Abulgasem Dakhil
Department of Anesthesia and Intensive Care, Faculty of Medical Technology, University of Tripoli, Tripoli, Libya.Author -
Mohamed Abuagela
Department of Anesthesia and Intensive Care, Faculty of Medical Technology, University of Tripoli, Tripoli, Libya.Author -
Abdul Aty Dakhil
Faculty of Science and Medical Technology, University of Tripoli, Tripoli, Libya.Author -
Wasim Elarbi
Department of Anesthesia and Intensive Care, Faculty of Medical Technology, University of Tripoli, Tripoli, LibyaAuthor -
Aisha Elansari
Department of Anesthesia and Intensive Care, Faculty of Medical Technology, University of Tripoli, Tripoli, LibyaAuthor
-
- Keywords:
- Uterine Fibroids, Age, Risk Factors, Symptoms, Diagnostic Device
- Abstract
-
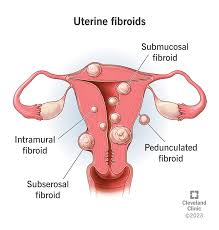
Uterine fibroids (leiomyomas) are common benign tumors of the uterus, composed of smooth muscle cells, fibroblasts, and fibrous extracellular matrix. While typically non-cancerous, some variants exhibit malignant potential. Their incidence and severity are influenced by race, with Black women developing fibroids earlier and experiencing more aggressive forms. Clinically, fibroids account for 30–50% of hysterectomies and impose substantial morbidity and healthcare costs on reproductive-aged women. This study aims to evaluate uterine fibroids among women, including the most common symptoms, risk factors, complications, and diagnostic devices. The research was designed to investigate complications and symptoms in 80 uterine fibroid patients at Tripoli Medical Center. 80 uterine fibroid patients (aged 17-45 years) revealed several key findings. The majority of participants were under 30 years old (48%), married (82.5%), and weighed 70-90 kg (55.25%). Cervicitis (45%) and hypertension (35%) emerged as the predominant risk factors, while abdominal cramps (60%) and irregular menstrual cycles (40%) were the most common symptoms. Trans-vaginal endoscopy served as the primary diagnostic method (55%), with 39% of patients experiencing pregnancy complications. Statistical analysis showed significant associations between younger age/marital status and cervicitis (p<0.05). These findings demonstrate that uterine fibroids predominantly affect younger women of reproductive age, with a strong association observed between certain demographic factors and specific risk factors. Notably, cervicitis showed significant associations with younger age and married status, while hypertension was particularly prevalent among patients with higher body weight.
- References
- Cover Image
-
- Downloads
- Published
- 2025-05-09
- Issue
- Volume 1, Issue 2, 2025
- Section
- Articles
How to Cite
Similar Articles
- Nadia Alrawaiq, Fatima Younis, Mabrouka Ismail, Identification and Evaluation of Drug-Related Problems in Patients with Reduced Kidney Function: A Retrospective Study , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 3, 2025
- Safa Mohammed Salim, Molecular Cytogenetic Study of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Patients Diagnosed in Erbil City Using Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization (FISH) Technique , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 2, 2025
- Mufeedah Mansour, Khoulah Alaribi, Prevalence and Outcomes of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci in Newborns Admitted to the NICU in a Tertiary Hospital in Libya , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 2, 2025
- Esam Alsaghair, Taher Alkesa, Wesam Elsaghayer, Validity of Selective Management in Trans pelvic Gunshot Wounds , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 2, 2025
- Ahmed Abu-Gharsa, Short-Term and Long-Term Outcomes of Mesh Versus Non-Mesh Repair in Emergency Inguinal Hernia Surgery , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 2, Issue 1, 2026
- Amhamad Alhajaji, Salem Almiladi, Ahmed Alhammali, Surgical Repair of Congenital Chest Wall Deformity (Pectus Excavatum): A 20-Year Multicenter Experience , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 1, 2025
- Hosam Elarabi, Salem Salem, Rajaa Fadel, Wafa Abozaid, Abdullah Ahmad, Ahmed Shtawa, Moftah Ali, Assessment of Fluoride Concentration in Drinking Water and Its Correlation with Dental Caries in Primary School Children in Gharyan, Libya , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 2, 2025
- Muftah Elbahloul, Khadija Amer, Sana Alghennai, Mohamed Jahan, Hussien Elaswdi, Manal Abusebbara, Ans Elkhodory, Mohamed Eshtiwi, Awareness of Nursing Staff in Misurata Public Health Facilities on HIV/AIDS Transmission: A Public Health, Anaesthesia, Healthcare Management and Health Education Concern , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 4, 2025
- Sara Fathi, Heba Hassan, Laila Alfageih, Prevalence of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae Isolated from Clinical Samples in Medical Tobruk Center , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 3, 2025
- Ali Madour, Haleemah Abdulrahman, Amani Alkawash, Rayan Alforgani, Saja Alzowaghi, Manal Alklabi, Eanas Elmaihub, Evaluation of Knowledge and Practice Toward Cystic Fibrosis Disease Among Medical Students and the Residents of Western Libya , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 3, 2025
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.








