Emerging Roles of Asprosin and Nesfatin-1 in Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes
- Authors
-
-
Al-Khazraji
College of Science, Diyala UniversityAuthor -
Rihab Mansoor
College of Science, Diyala UniversityAuthor -
Shahad Alwan
College of Science, Diyala UniversityAuthor -
Anfal Abed
College of Science, Diyala UniversityAuthor -
Alaa Mahmoud
Department of Medical Laboratory Technologies, Al-Amarah University College, IraqAuthor -
Safaa Ahmed
College of Science, Diyala UniversityAuthor
-
- Keywords:
- Asprosin; Nesfatin-1; T2DM; Obesity, Glucose
- Abstract
-
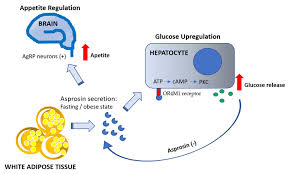
The global surge in diabetes and obesity underscores the role of adipokines. Asprosin disrupts glucose homeostasis, while nesfatin-1 may offer protective effects. This study investigated their serum levels in poorly controlled T2DM and associations with hyperglycemia and obesity. The study included 110 type 2 diabetes patients and 70 healthy controls, aged 40–70 years. Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) and glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) were measured using the Roche Cobas Integra 400 Plus. Serum asprosin and nesfatin-1 levels were quantified by ELISA, and body mass index (BMI) was calculated as weight/height². T2DM patients exhibited significantly higher serum levels of asprosin and nesfatin-1 compared to controls (p < 0.001). A significant positive correlation was observed between asprosin and nesfatin-1, as well as between nesfatin-1 and disease duration (p = 0.01). Serum asprosin was strongly associated with glucose levels, whereas neither biomarker showed a significant correlation with BMI. Elevated asprosin and nesfatin-1 levels in poorly controlled T2DM patients contribute to disease mechanisms. Increased nesfatin-1 represents a compensatory mechanism to mitigate insulin deficiency, highlighting its potential as a predictive biomarker.
- References
- Cover Image
-
- Downloads
- Published
- 2025-09-05
- Issue
- Volume 1, Issue 3, 2025
- Section
- Articles
How to Cite
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- Shahad Alwan, Molecular detection of the MexA efflux pump gene in Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from Diyala Province , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 3, 2025
Similar Articles
- Fozia Aborayana, Fadila Elghadban, Souad Aboalqasim, Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus and the Pregnancy Outcomes: A Retrospective Study in the Pediatrics Department of Tripoli University Hospital – Tripoli, Libya , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 2, 2025
- Mahmoud Ashawesh, Mustafa Alkawash, Ayah Meigal, Baraah Almsiri, Abtihal Almasalati, Tracking the Burden of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Among Libyan Patients in Three Populated Districts of Tripoli, Libya , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 4, 2025
- Al Basher Alafi, Ahmed Ashtawa, Siddig Bushra Mohamed, Marwa Al Mabrok, Waed Aldaekh, Hebah Zahmoul, Obesity and Headache in Libyan Adults: Findings from a Descriptive Cross‑Sectional Study in Gharyan City , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 2, Issue 1, 2026
- Fayrouz Khaled, Sarah Mohammed, Investigating the Impact of Creatine and Vitamin C Supplementation on Insulin Sensitivity and Glycated Hemoglobin Levels in Male Rabbits , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 3, 2025
- Zinab Elfituri, Huria Dardar, Yasmein Alshibani, Aml Koubas, Entisar Aboukanda, Abdalhalim Suaiee, The Impact of Lifestyle Factors on Arterial Blood Pressure and Its Control in Hypertensive Patients , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 2, 2025
- Marfoua Ali, Faraj Sulayman, Elham keeshar, General Health Parameters in Children Aged 6–10 Years in El‑Beyda, Libya , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 2, Issue 1, 2026
- Sara Taeb, Ghufran Dehoom, Khuloud Ajaj, Comparison of the Efficacy of Inositol-Containing Medication Only versus Metformin and Inositol among Libyan Infertile Women with Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 3, 2025
- Ahmed Atia, Antibiotic Resistance in Libya and the Prevalence of Antibiotic Self-Medication: A Review , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 1, 2025
- Hawa Abduljalil, Tarik Enaairi, Striae Gravidarum and Its Effect on the Quality of Life Index in Libyan Pregnant Women , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 1, 2025
- Abulgasem Dakhil, Mohamed Abuagela, Abdul Aty Dakhil, Wasim Elarbi, Aisha Elansari, Evaluation of Uterine Fibroids Among Women in Tripoli , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 2, 2025
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.








