Evaluation of Uterine Fibroids Among Women in Tripoli
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.69667/rmj.25201Keywords:
Uterine Fibroids, Age, Risk Factors, Symptoms, Diagnostic DeviceAbstract
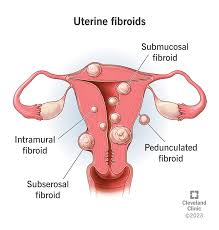
Uterine fibroids (leiomyomas) are common benign tumors of the uterus, composed of smooth muscle cells, fibroblasts, and fibrous extracellular matrix. While typically non-cancerous, some variants exhibit malignant potential. Their incidence and severity are influenced by race, with Black women developing fibroids earlier and experiencing more aggressive forms. Clinically, fibroids account for 30–50% of hysterectomies and impose substantial morbidity and healthcare costs on reproductive-aged women. This study aims to evaluate uterine fibroids among women, including the most common symptoms, risk factors, complications, and diagnostic devices. The research was designed to investigate complications and symptoms in 80 uterine fibroid patients at Tripoli Medical Center. 80 uterine fibroid patients (aged 17-45 years) revealed several key findings. The majority of participants were under 30 years old (48%), married (82.5%), and weighed 70-90 kg (55.25%). Cervicitis (45%) and hypertension (35%) emerged as the predominant risk factors, while abdominal cramps (60%) and irregular menstrual cycles (40%) were the most common symptoms. Trans-vaginal endoscopy served as the primary diagnostic method (55%), with 39% of patients experiencing pregnancy complications. Statistical analysis showed significant associations between younger age/marital status and cervicitis (p<0.05). These findings demonstrate that uterine fibroids predominantly affect younger women of reproductive age, with a strong association observed between certain demographic factors and specific risk factors. Notably, cervicitis showed significant associations with younger age and married status, while hypertension was particularly prevalent among patients with higher body weight.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
How to Cite
Similar Articles
- Mariam Alqasser, Stroke Incidence and Risk Profile in Misrata City: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Hospital-Based Study from Emergency Medical Records (2019–2020) , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 4, 2025 (October to December)
- Hasna Akub, Tawfeek Altawaty, Aun Youis, Seroprevalence of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection and Demographic Correlates among Individuals Tested in Al-Jabal Al-Akhdar, Eastern Libya: A Cross-Sectional Laboratory-Based Study , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 4, 2025 (October to December)
- Zinab Elfituri, Huria Dardar, Yasmein Alshibani, Aml Koubas, Entisar Aboukanda, Abdalhalim Suaiee, The Impact of Lifestyle Factors on Arterial Blood Pressure and Its Control in Hypertensive Patients , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 2, 2025
- Sarah Alfaqaih, Nawara Ghlio, Parental Stress and Childhood Cancer in Libya: A Cross-Sectional Study in Misurata , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 3, 2025
- Md Sayed Ali Sheikh, Umme Salma, Maternal Plasma Lipid Profile as a Potential Risk Factor for Spontaneous Preterm Labor , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 2, 2025
- Fozia Aborayana, Fadila Elghadban, Souad Aboalqasim, Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus and the Pregnancy Outcomes: A Retrospective Study in the Pediatrics Department of Tripoli University Hospital – Tripoli, Libya , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 2, 2025
- Nadia Alrawaiq, Fatima Younis, Mabrouka Ismail, Identification and Evaluation of Drug-Related Problems in Patients with Reduced Kidney Function: A Retrospective Study , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 3, 2025
- Basheer Alhadheeri, Comorbidities and Treatment Outcomes of Acute Appendicitis at a Tertiary Center in Libya , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 3, 2025
- Safaa Shehab, Hiba Awad, Shahrazad Khalaf, Zahraa Dawood, Sabaa Kareem, Fatima Salman, Blood-borne Viral Infections in Hemodialysis Units in Iraq: A Narrative Review of Prevalence and Contributing Factors , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 3, 2025
- Safa Mohammed Salim, Molecular Cytogenetic Study of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Patients Diagnosed in Erbil City Using Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization (FISH) Technique , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 2, 2025
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.








