Striae Gravidarum and Its Effect on the Quality of Life Index in Libyan Pregnant Women
- Authors
-
-
Hawa Abduljalil
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, National Cancer Institute, Misrata, LibyaAuthor -
Tarik Enaairi
Department of Dermatology, National Cancer Institute, Misrata, Libya.Author
-
- Keywords:
- Striae gravidarum, quality of life, Libyan pregnant women, Skindex-16, stretch marks
- Abstract
-
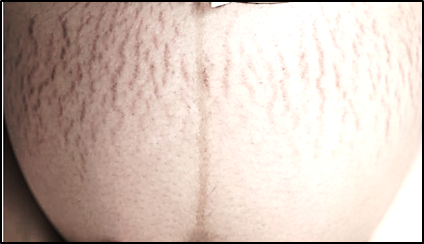
Striae gravidarum (SG) are common cutaneous changes during pregnancy, affecting up to 90% of women worldwide. Traditionally viewed as physiological cosmetic skin changes, emerging evidence suggests that SG may impose significant psychological distress and adversely affect quality of life (QoL). This study was conducted to evaluate the impact of SG on dermatology-specific QoL in Libyan pregnant women, taking into account established risk factors, cultural perceptions, and recent advances in therapeutic interventions. This cross-sectional study (January 2024 – December 2024) evaluated 150 pregnant women (aged ≥18) with striae gravidarum. Participants with systemic diseases or using corticosteroids were excluded. Data were collected using a self-administered online questionnaire that integrated clinical and psychosocial assessments. SG severity was determined via Davey’s scoring system, and quality of life was measured with the Skindex-16 questionnaire, validated against WHOQOL-BREF. Data analysis was performed using SPSS v25, with p < 0.05 considered statistically significant. Among 150 Libyan women with striae gravidarum (SG), 72% were aged 20–40 years, 36.7% had ≥4 pregnancies, and 64% reported a family history of SG. Participants experienced significant postpartum weight gain (73.2 ± 12.6 kg vs. pre-pregnancy 64.5 ± 10.8 kg, p < 0.001). SG was most prevalent on the abdomen (76%) and thighs (54%). Rapid weight gain (52.7%) and multiparity (32%) were perceived as leading causes. Emotional/social impacts included embarrassment (45.3%), mild self-esteem concerns (29.3%), and partner-related challenges (26.7%). Quality of life (QoL) scores (median: 16.5) were significantly higher in older women (>40 years, p < 0.001) and those with a family history of SG (p = 0.015). SG exerts a substantial negative effect on the dermatology-specific QoL of Libyan pregnant women, with pronounced impacts on emotional health and daily functioning.
- References
- Cover Image
-
- Downloads
- Published
- 2025-04-11
- Issue
- Volume 1, Issue 1, 2025
- Section
- Articles
How to Cite
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- Tarik Enaairi, Sundus Aldeebani, Hawa Abduljalil, Buschke-Fischer-Brauer Keratosis Punctata of the Palmar Creases in A 45-Year-Old Libyan Female: A Case Report , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 3, 2025
Similar Articles
- Amhamad Alhajaji, Salem Almiladi, Ahmed Alhammali, Surgical Repair of Congenital Chest Wall Deformity (Pectus Excavatum): A 20-Year Multicenter Experience , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 1, 2025
- Mahmud Abushhewa, Mohamed Agilla, Ashraf Naass, Khadega Alazoumi, Abdulati Salem, Taj Al-Din Jaber, Mohammed Abdulqadir, Knowledge, Attitude, and Practices about Antibiotic Misuse among Libyan Community: A Cross-Sectional Survey , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 3, 2025
- Abulgasem Dakhil, Mohamed Abuagela, Abdul Aty Dakhil, Wasim Elarbi, Aisha Elansari, Evaluation of Uterine Fibroids Among Women in Tripoli , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 2, 2025
- Adell Abubakeer, Nabel Mansour, The Association Between ABO and Rhesus Blood Groups and Diabetes Mellitus in Libya: A Systematic Review of National Evidence , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 3, 2025
- Hasna Akub, Tawfeek Altawaty, Aun Youis, Seroprevalence of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection and Demographic Correlates among Individuals Tested in Al-Jabal Al-Akhdar, Eastern Libya: A Cross-Sectional Laboratory-Based Study , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 4, 2025
- Sara Fathi, Heba Hassan, Laila Alfageih, Prevalence of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae Isolated from Clinical Samples in Medical Tobruk Center , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 3, 2025
- Salem Elfard, Zinab Elfituri, Integration of Social and Behavioral Sciences (SBS) in Undergraduate Libyan Medical Education Programs , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 3, 2025
- Tarik Enaairi, Sundus Aldeebani, Hawa Abduljalil, Buschke-Fischer-Brauer Keratosis Punctata of the Palmar Creases in A 45-Year-Old Libyan Female: A Case Report , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 3, 2025
- Fatima Elhag Ahmed, Susan Zroog, Abdelhakam Ali, Nurses' Knowledge regarding Immediate Care of Newborns in the Saudi Hospital for Obstetrics and Gynecology, Sudan , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 3, 2025
- Faiza Nouh, Salima Elfagi, Mohamed Buzqeia, Ahlam Adel, Mawadda salah, Enas Hassan, Safa Edress, Determinants of Food Choices in University Cafeterias: A Cross-Sectional Study Among Public Health Students in Libya , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 4, 2025
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.








