The Role of Immune Response in Bacterial Urinary Tract Infections in Iraq: A Review
- Authors
-
-
Shahrazad Ahmed
Department of Forensic Science, College of Sciences, Diyala University, Diyala, IraqAuthor -
Neyaf Alageedi
Department of Biology, College of Sciences, Diyala University, Diyala, IraqAuthor -
Eman Muhsin
Research and Technology Center of Environment, Water and Renewable Energy, Scientific Research Commission, Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research, 11001, Iraq.Author -
Doaa Abdulwahab
Department of Forensic Science, College of Sciences, Diyala University, Diyala, IraqAuthor
-
- Keywords:
- Urinary Tract Infections, Bacterial UTIs, Antibiotic Resistance, Immune System, Iraq.
- Abstract
-
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are among the most prevalent bacterial infections, frequently caused by uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC), the primary causative agent in humans. The immune system plays a critical role in defending against bacterial UTIs by preventing pathogen attachment and colonization in the urinary epithelium, while also mitigating infection severity through innate and adaptive immune responses. This review examines previous studies conducted in Iraq on the immunological aspects of bacterial UTIs. It explores the mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in UTI-causing bacteria and synthesizes findings from 42 studies that investigate the role of innate and adaptive immunity in UTI-related inflammation. Iraqi research has consistently demonstrated a high prevalence of multidrug-resistant (MDR) UPEC strains, underscoring the urgent need for immune-based interventions, such as vaccines and immunomodulatory therapies, to enhance host defenses and reduce dependence on antibiotics. Key findings highlight the involvement of neutrophils, cytokines, and antimicrobial peptides in immune defense against UPEC, while bacterial immune evasion strategies contribute to recurrent infections. This review also emphasizes the necessity for personalized medicine approaches that integrate genetic and immunological insights to improve UTI prediction, prevention, and treatment in the Iraqi population. Numerous Iraqi studies have reinforced the crucial role of innate immunity in determining UTI susceptibility. A deeper understanding of immune mechanisms in UTI pathogenesis is essential for developing more effective treatment strategies and alleviating the burden of recurrent infections.
- References
- Cover Image
-
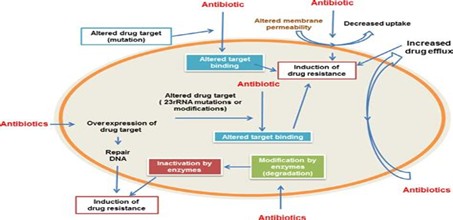
- Published
- 2025-05-14
- Issue
- Volume 1, Issue 2, 2025
- Section
- Articles
How to Cite
Similar Articles
- Milad Elshah, Mohamed Zeglam, Asmaa Abdeewi, In vitro Comparison of Fracture Toughness Among Three CAD/CAM Fixed Prosthodontic Materials , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 4, 2025
- Ahmed Atia, Eshraq Alsherif, Astabraq Ali, Raghad Nour Aldden, Samar Mohammed, Additive Effect of High Sugar Intake and Prolonged Screen Exposure on Cognitive Performance in Young Adults , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 2, Issue 1, 2026
- Suad Altubouli, Hana Hafalish, Marfoua Ali, Serum 25-Hydroxy Vitamin D Levels and Disease Severity in Pediatric Atopic Dermatitis: An Inverse Correlation , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 2, Issue 1, 2026
- Fathy Awad, Nisreen Abdulali, Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii Infection and Its Association with Gender and Age among Patients Attending Al-Bayda Medical Center, Libya , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 2, Issue 1, 2026
- Mahmoud Ashawesh, Mustafa Alkawash, Ayah Meigal, Baraah Almsiri, Abtihal Almasalati, Tracking the Burden of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Among Libyan Patients in Three Populated Districts of Tripoli, Libya , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 4, 2025
- Ahmed Alsharksi, Abdalla Ali, Adam Mustapha, Clostridium difficile A-B Toxins as a Cause of Diarrheal Disease: Data from a University Hospital in Northern Cyprus , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 4, 2025
- Adell Abubakeer, Nabel Mansour, The Association Between ABO and Rhesus Blood Groups and Diabetes Mellitus in Libya: A Systematic Review of National Evidence , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 3, 2025
- Al-Khazraji , Rihab Mansoor, Shahad Alwan, Anfal Abed, Alaa Mahmoud, Safaa Ahmed, Emerging Roles of Asprosin and Nesfatin-1 in Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 3, 2025
- Fozia Aborayana, Fadila Elghadban, Souad Aboalqasim, Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus and the Pregnancy Outcomes: A Retrospective Study in the Pediatrics Department of Tripoli University Hospital – Tripoli, Libya , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 2, 2025
- Hosam Elarabi, Salem Salem, Rajaa Fadel, Wafa Abozaid, Abdullah Ahmad, Ahmed Shtawa, Moftah Ali, Assessment of Fluoride Concentration in Drinking Water and Its Correlation with Dental Caries in Primary School Children in Gharyan, Libya , Razi Medical Journal: Volume 1, Issue 2, 2025
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.








